Recap of DCConnect at Capacity Europe 2025
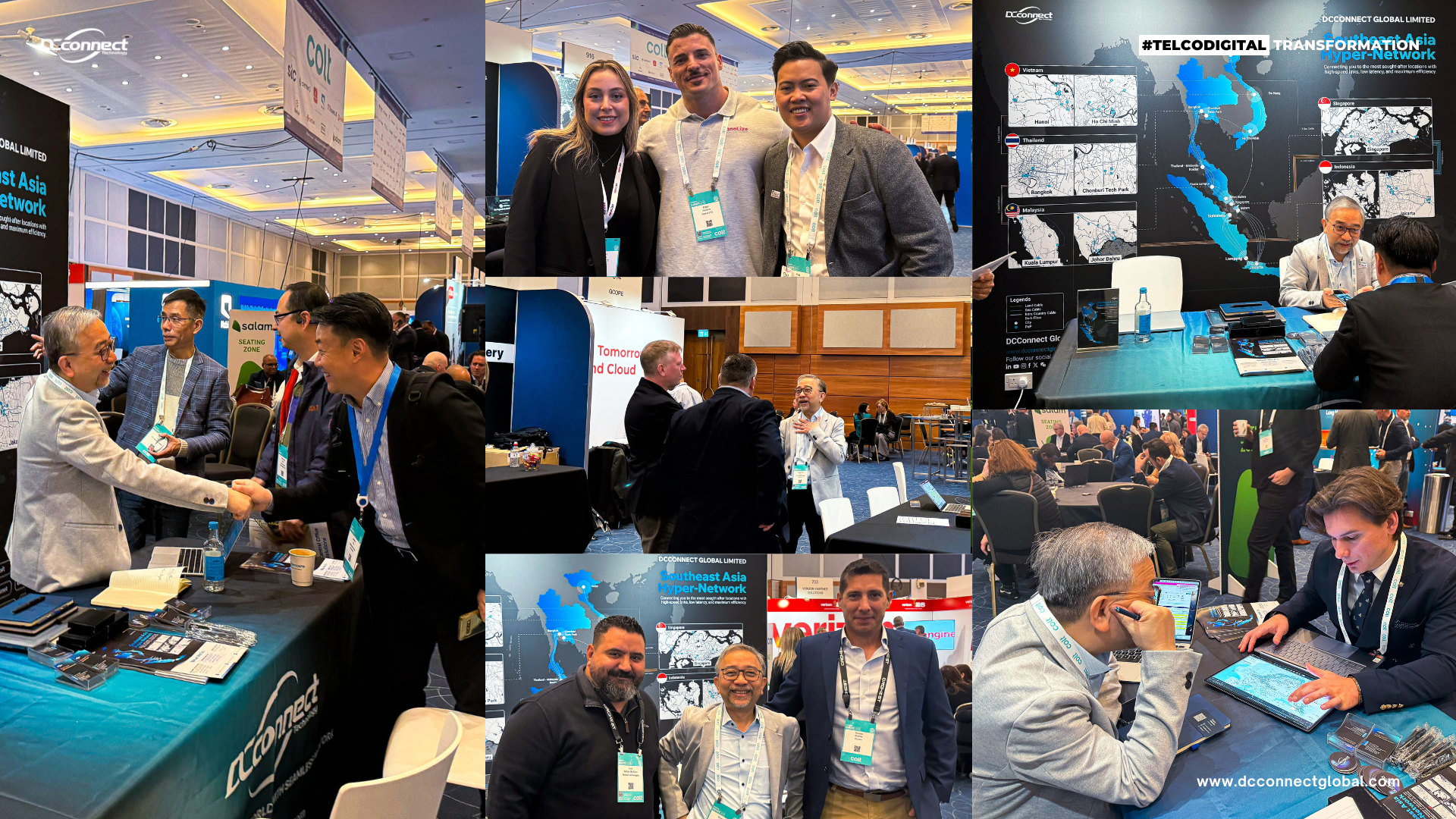
What a week it’s been at Capacity Europe 2025! As the industry gathered in London once again, the energy on the floor was nothing short of electric and DCConnect was right at the center of it. Booth 911: The Place Where Europe Got Its First Look at Southeast Asia’s Next-Level Connectivity This year, we brought something special to Europe: the most in-demand hyper-connectivity capabilities from Southeast Asia, delivered through a carrier-neutral, automated approach that continues to reshape how global networks interconnect. The curiosity and forward-thinking conversations reminded us exactly why Capacity Europe remains one of the most important gatherings for the global connectivity ecosystem. To everyone who stopped by, thank you. Our collaboration are what keep this industry moving. Award Win: Best Network Technology & Software Development One of the biggest highlights of the week came during the Global Connectivity Awards 2025, where DCConnect was named the winner of Best Network Technology & Software Development We submitted our flagship platform, DC Gateway, and were honored to be chosen among an outstanding group of finalists. The judging panel shared: “The provider secured the award by transforming complex global connectivity into a streamlined, automated platform, differentiating itself through radical carrier-neutral collaboration.” This recognition means a lot to our entire team. DC Gateway was built for one purpose: to make global connectivity simpler, faster, and more transparent. Receiving this award reinforces our mission and energizes us to push even further. Looking Ahead Capacity Europe 2025 reminded us of something important: the industry is moving faster than ever, and collaboration is the force driving that momentum. As we head into another year of growth and innovation, we’re more committed than ever to building a seamless, automated future for global telecommunications. Thank you to everyone who made this year’s event unforgettable. See you next year—stronger, bigger, and even more connected.