What Is Internet Exchange (IX)?
Internet Exchange (IX) is a physical and virtual infrastructure where networks connect and exchange traffic directly. Instead of sending data through long transit routes, participants can peer within the same ecosystem.
As a result, traffic becomes faster, latency decreases, and bandwidth usage becomes more efficient. For digital businesses, performance is critical because user experience directly affects revenue and trust.
Why IX Participation Is Important for Modern Networks
Today, enterprises, content providers, and cloud platforms must deliver services instantly. However, relying only on upstream transit providers often creates longer paths and unpredictable performance.
By joining an IX platform, networks route traffic more efficiently. Moreover, they gain better control, stronger redundancy, and reduced dependency on single providers.
Because of this, peering strategy has become essential for organizations that want consistent service quality and scalability.
How Peering Through an IX Works
The model is simple.
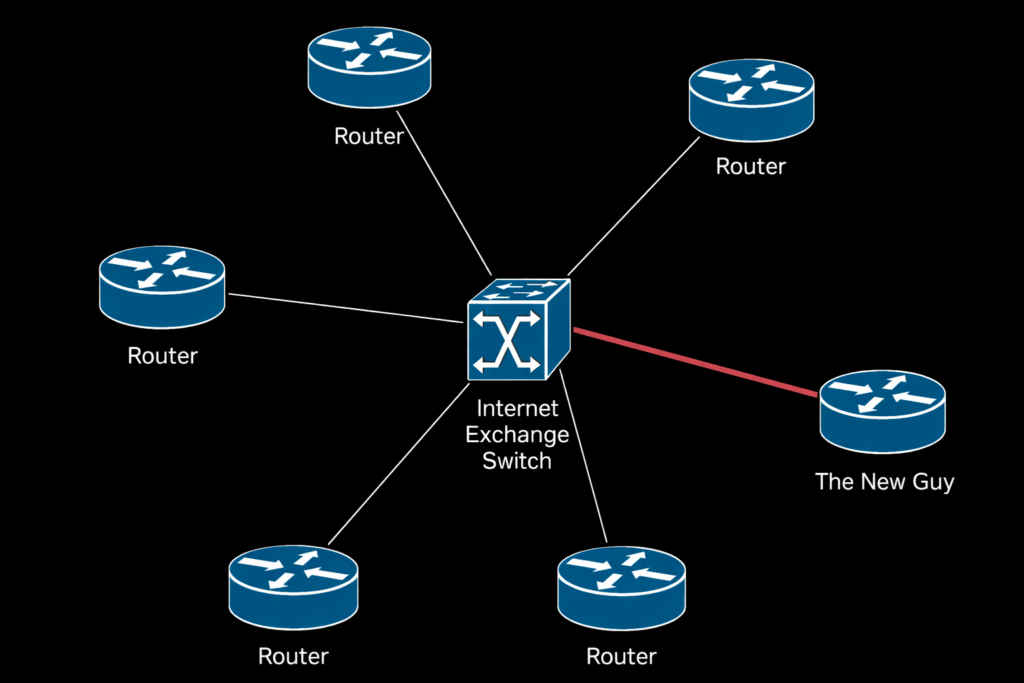
Network Connection
Participants connect routers to the switching fabric.
Peering Sessions
They establish agreements to exchange traffic.
Direct Routing
Data moves between networks without unnecessary detours.
Performance Gains
Therefore, users experience lower latency and improved stability.
Internet Exchange Topology Example
Key Benefits of Peering
Lower Latency
Direct routing shortens the delivery path.
Cost Optimization
Moreover, organizations can reduce dependency on expensive transit bandwidth.
Higher Reliability
Networks gain alternative paths during outages.
Better Throughput
Because congestion is minimized, performance becomes more predictable.
Strong Ecosystem Access
Participants can reach content providers, ISPs, and cloud platforms in one place.
Who Should Connect to an IX Platform?
This connectivity model is ideal for internet service providers, SaaS platforms, financial services, content networks, and enterprises serving regional or global users.
If digital delivery is important to your business, direct interconnection offers a competitive edge.
How IX Connectivity Drives Competitive Advantage
Organizations connected through peering environments gain measurable routing efficiency. As a result, applications respond faster and customer satisfaction increases.
Moreover, traffic exchange reduces reliance on transit vendors. Therefore, businesses can manage growth while maintaining predictable spending.
Limitations of Physical Participation
Despite the benefits, joining an exchange physically can be difficult.
Companies often deal with cross-connect fees, hardware installation, long deployment times, and geographic constraints. For many businesses, this slows expansion.
Why Choose DCConnect Remote Peering?
DCConnect simplifies access to major ecosystems.
No On-Site Equipment
Businesses can join without deploying routers at the facility.
Faster Activation
Moreover, services are delivered quicker than traditional builds.
Private and Secure Transport
Traffic runs on dedicated infrastructure rather than the open internet.
Multi-Exchange Reach
A single connection can provide access to multiple markets.
Operational Simplicity
In addition, DCConnect supports integration so internal teams stay focused on their platforms.
Integration Beyond Peering
Organizations can also combine this connectivity with broader interconnection strategies to enhance hybrid and multi-cloud performance.
According to coordination by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, efficient routing between networks is fundamental to global internet stability.
Conclusion
Direct traffic exchange enables faster, smarter, and more efficient delivery. Peering improves latency, reliability, and cost management.
However, physical presence is not always practical.
With DCConnect Remote Peering, organizations can securely access leading ecosystems without infrastructure burden while maintaining scalability and operational simplicity.
